The Evolution of Data Analytics Tools Over the Years
- k86874248
- Feb 21, 2025
- 4 min read
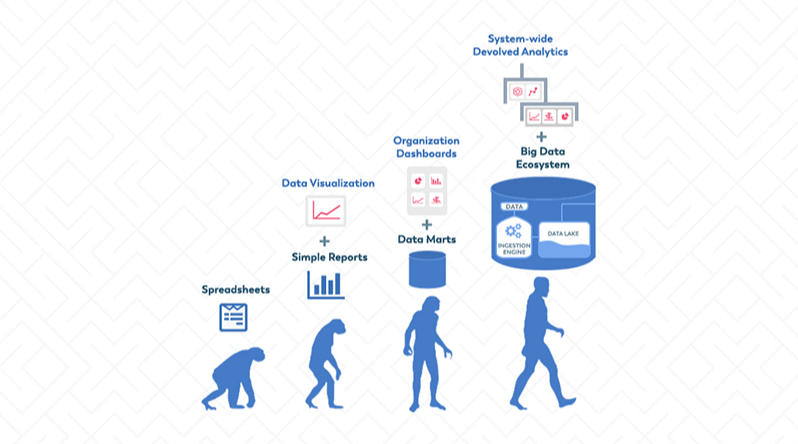
Data analytics has revolutionized industries across the world by providing insights that drive business decisions, improve efficiency, and enhance customer experiences. Over the years, data analytics tools have evolved significantly, adapting to changing technologies, business needs, and data complexity. This article explores the evolution of data analytics tools, from their early beginnings to the cutting-edge solutions we use today.
Early Days of Data Analytics
In the early stages, data analysis was a manual process, relying heavily on traditional methods like spreadsheets. Analysts would gather data from different sources, manually input the data into systems, and perform calculations to derive insights. During this period, tools like Microsoft Excel played a critical role in data management and analysis. However, these tools were limited in handling large datasets, processing complex queries, and effectively visualizing data.
The Rise of Relational Databases
As data grew in volume and complexity, businesses needed more advanced systems. This led to the rise of relational databases in the 1980s and 1990s. Tools like Oracle Database and SQL Server enabled organizations to store large amounts of structured data and perform queries more efficiently. With the introduction of Structured Query Language (SQL), data analysts could retrieve and manipulate data more easily.
These relational database management systems (RDBMS) formed the backbone of data storage and analysis, providing more flexibility and accuracy. They allowed businesses to manage customer information, financial data, inventory, and more in a structured way. However, while relational databases were excellent for structured data, they struggled with handling unstructured data, such as text, images, and videos.
The Emergence of Business Intelligence Tools
As the need for more accessible data analysis grew, Business Intelligence (BI) tools emerged in the 1990s and 2000s. These tools were designed to help organizations analyze data and generate reports without requiring deep technical expertise. Popular BI tools like Tableau, Power BI, and QlikView enabled users to create interactive dashboards, visualize trends, and make data-driven decisions with ease.
With the rise of BI tools, the ability to extract insights from data became more democratized. Non-technical users could now engage with data and gain valuable insights, fostering a data-driven culture within organizations. The user-friendly nature of these tools and their ability to process large datasets made them essential for businesses aiming to stay competitive in an increasingly data-centric world.
Big Data and the Shift Toward Advanced Analytics
The growth of the internet and digital technologies led to an explosion in data volume, variety, and velocity, resulting in the advent of Big Data. Big Data analytics tools were developed to handle the massive amounts of unstructured data generated by social media, sensors, mobile devices, and more. Hadoop and Apache Spark became popular frameworks for processing and analyzing big data. These tools allowed businesses to store and analyze data in distributed systems, enabling faster and more efficient processing.
NoSQL databases, such as MongoDB and Cassandra, also gained popularity as they offered more flexibility in storing unstructured data. Unlike traditional relational databases, NoSQL databases could scale horizontally and handle a variety of data types, making them ideal for big data applications.
Moreover, predictive analytics emerged during this period. Predictive models used statistical algorithms and machine learning techniques to forecast future trends based on historical data. Businesses began using tools like SAS, R, and Python to develop predictive models that informed marketing strategies, supply chain management, and financial forecasting.
The Age of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
In recent years, the field of data analytics has been transformed by Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML). These technologies enable data analytics tools to go beyond traditional analysis and make autonomous decisions based on data. AI-powered tools like Google Analytics 360, IBM Watson Analytics, and DataRobot leverage ML algorithms to uncover patterns, optimize processes, and generate real-time insights.
Machine learning models are now integrated into many analytics platforms, making it easier for organizations to build and deploy predictive models. These tools can analyze vast amounts of data, identify correlations, and predict outcomes with remarkable accuracy. As a result, businesses are able to automate decision-making processes, personalize customer experiences, and improve operational efficiency.
Cloud Computing and Data Analytics
With the growth of cloud computing, businesses can now store and process data on scalable, on-demand platforms. Cloud-based analytics tools like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Microsoft Azure have democratized data analytics by making high-powered tools accessible to companies of all sizes. These platforms offer scalable storage, advanced analytics capabilities, and integrations with machine learning and AI tools.
Cloud computing has also simplified collaboration, allowing teams to work with real-time data and share insights seamlessly. Additionally, cloud-native analytics tools have enabled businesses to reduce infrastructure costs, increase security, and ensure better performance.
Real-Time Analytics and Streaming Data
As businesses strive to respond to fast-paced market changes, real-time analytics has become a key trend. Tools like Apache Kafka, Apache Flink, and Google BigQuery enable the processing of streaming data, allowing businesses to analyze and act on data in real time. This is particularly useful for industries like finance, e-commerce, and healthcare, where timely insights can drive critical decisions.
Real-time analytics empowers organizations to detect anomalies, monitor performance, and make proactive decisions without waiting for batch processing. It enables businesses to respond to changing conditions, such as market fluctuations, customer behavior, and operational issues, faster than ever before.
Conclusion
The evolution of data analytics tools has been remarkable, progressing from manual spreadsheets to advanced AI-driven platforms. Today, organizations can analyze data faster and more accurately using business intelligence, predictive analytics, machine learning, and real-time analytics. As the field continues to evolve, emerging technologies like quantum computing and edge analytics will further transform data processing. For those looking to enhance their skills, a Data Analytics course in Noida, Delhi, Lucknow, Nagpur, and other cities in India can provide the necessary expertise to stay competitive in this data-driven world. Embracing these tools and technologies is crucial for future success.



Comments